Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
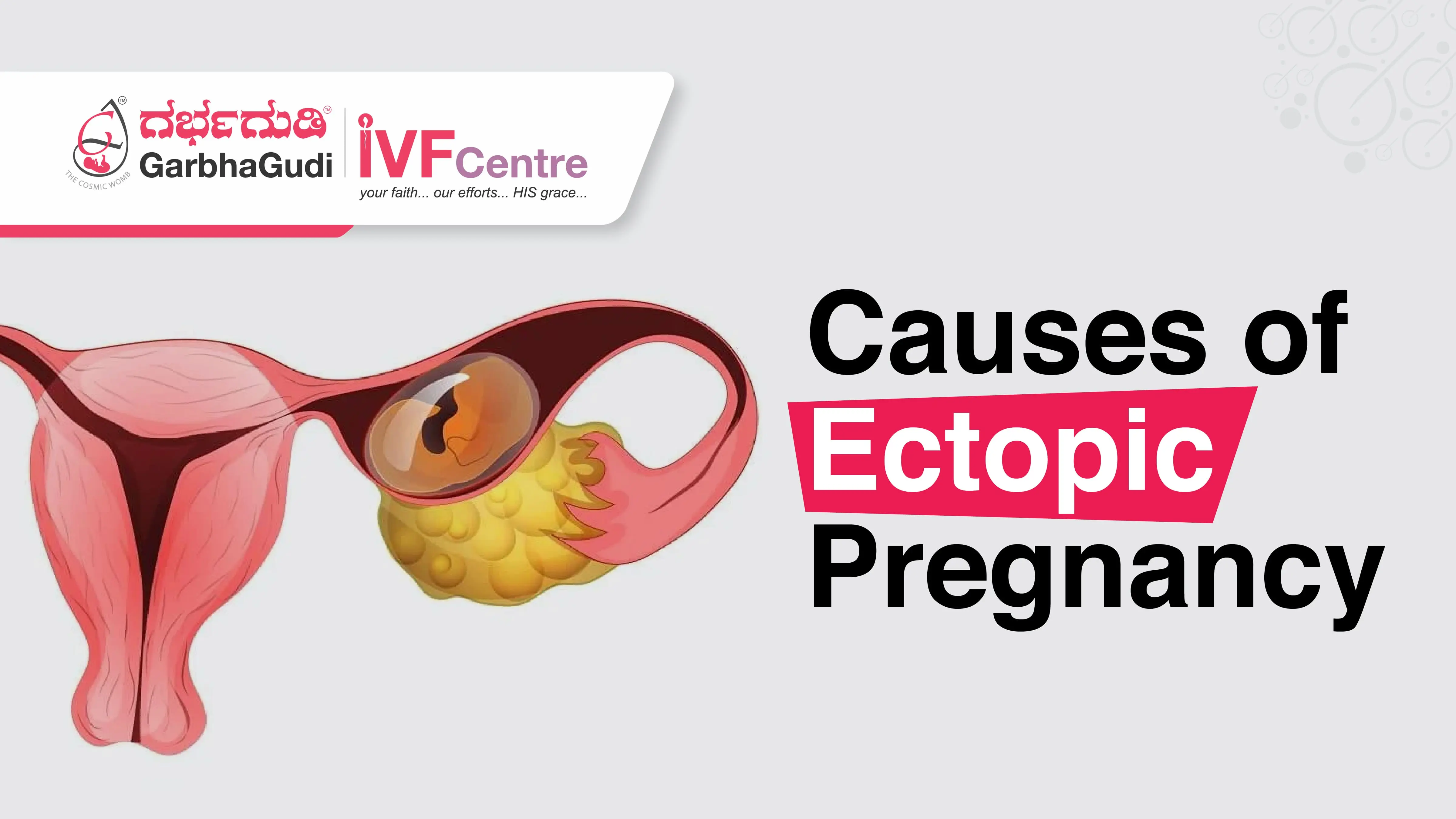
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening condition in which a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus, where a normal pregnancy develops. The majority of ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tubes, which is why they are often called tubal pregnancies. However, in rare cases, the fertilized egg may implant in other locations such as the ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity.
Why Does Ectopic Pregnancy Occur?
For a pregnancy to proceed normally, the fertilized egg travels from the ovary through the fallopian tube and into the uterus, where it implants in the uterine lining. In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg gets stuck or implants in an area outside the uterus. This abnormal implantation is often due to:
Damage or blockage in the fallopian tubes (caused by infections, previous surgeries, or medical conditions).
Hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities in the reproductive system.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Early symptoms may mimic those of a normal pregnancy, such as a missed period, nausea, or breast tenderness. However, as the pregnancy progresses, signs of an ectopic pregnancy may include:
Sharp or cramping pain on one side of the abdomen or pelvis.
Vaginal bleeding or spotting that differs from a regular period.
Shoulder pain (a sign of internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm).
Dizziness, fainting, or shock (from severe internal bleeding if the fallopian tube ruptures).
Why Is It Dangerous?
Ectopic pregnancies cannot result in a viable baby and can endanger the mother’s life if not treated promptly. If the growing pregnancy ruptures the fallopian tube or another organ, it can lead to severe internal bleeding, infection, or even death.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose ectopic pregnancy using:
Ultrasound: To check the location of the pregnancy.
Blood tests: To measure the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which may rise abnormally in ectopic pregnancies.
In some cases, exploratory surgery may be needed if the diagnosis is unclear.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on how early the condition is detected and the overall health of the mother:
Medication: Methotrexate is often prescribed to halt the growth of the pregnancy. This option is used if the ectopic pregnancy is caught early and the fallopian tube hasn’t ruptured.
Surgery: If the ectopic pregnancy is advanced or causing complications, surgical intervention is necessary. A laparoscopic procedure may remove the ectopic tissue while preserving the fallopian tube if possible. In severe cases, the affected fallopian tube may need to be removed.
Future Fertility After Ectopic Pregnancy
Many women can conceive again after an ectopic pregnancy, but the risk of recurrence is higher. It’s essential to address underlying causes, such as infections or tube damage, and work closely with a fertility specialist for future pregnancies.
Preventing Ectopic Pregnancy
While not all ectopic pregnancies are preventable, reducing risk factors can help:
Treat pelvic infections promptly.
Avoid smoking.
Use fertility treatments with caution under medical supervision.
Discuss risks with your doctor if you have a history of ectopic pregnancies or fallopian tube surgeries.
Early detection and timely medical care are crucial to manage ectopic pregnancies safely and to preserve future fertility
What are the main causes of ectopic pregnancy?
The main causes of ectopic pregnancy involve conditions that disrupt the normal movement of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes and into the uterus. These causes can result from anatomical, hormonal, or medical factors. Below is a detailed explanation of the key causes:
1. Previous Ectopic Pregnancy
Women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of having another. This may be due to residual damage or scarring in the fallopian tubes.
2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Infections in the reproductive organs, particularly those caused by sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea, can lead to scarring and inflammation of the fallopian tubes. This can prevent the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus.
3. Surgery on Fallopian Tubes
Previous surgeries, such as tubal ligation (sterilization), tubal reversal, or surgery to remove blockages, can damage the tubes or create scar tissue. This increases the likelihood of the egg implanting in the tube.
4. Congenital or Structural Abnormalities
Some women may have abnormally shaped fallopian tubes or uterine structures due to birth defects or conditions like endometriosis. These abnormalities can make it harder for the fertilized egg to travel to the uterus.
5. Endometriosis
Endometriosis causes uterine-like tissue to grow outside the uterus, often leading to scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes, which may result in an ectopic pregnancy.
6. Fertility Treatments
Women undergoing assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF), have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancies. This may be because fertility treatments bypass the natural journey of the egg through the fallopian tube.
7. Use of Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
While rare, pregnancies that occur with an IUD in place are more likely to be ectopic. The IUD’s mechanism reduces the chance of a uterine pregnancy, increasing the relative risk of ectopic implantation.
8. Hormonal Imbalances
Disruptions in hormonal levels can affect the proper functioning of the fallopian tubes, impairing the transport of the egg to the uterus.
9. Smoking
Smoking damages the fallopian tubes and alters their function. It increases the risk of an ectopic pregnancy because the egg may fail to reach the uterus.
10. Age and Health Conditions
Women over 35 have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy due to age-related changes in reproductive health.
Health conditions such as diabetes or pelvic adhesions from previous infections or surgeries may also contribute.
Combination of Factors
Often, multiple factors contribute to an ectopic pregnancy, such as having both a history of PID and smoking. Identifying and addressing these risks can help reduce the chances of an ectopic pregnancy.
If you suspect you’re at risk or experience symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, consult a healthcare provider immediately for evaluation and treatment
Can an ectopic pregnancy occur without any known risk factors?
Yes, an ectopic pregnancy can occur even without any known risk factors. While certain conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease, previous ectopic pregnancies, or fallopian tube damage significantly increase the likelihood, a considerable number of ectopic pregnancies arise in women who have no identifiable risk factors.
Why Can This Happen?
Subtle or Unrecognized Factors:
Some underlying causes, such as minor infections, hormonal imbalances, or anatomical issues, may go undiagnosed or unnoticed.Spontaneous Occurrence:
In some cases, no specific cause can be determined, and the pregnancy may implant outside the uterus due to random or unpredictable events.Unknown Medical Conditions:
Early-stage conditions like mild endometriosis, small fibroids, or unreported tubal damage may not show noticeable symptoms but could contribute to ectopic pregnancy.
How Common Is It?
While many ectopic pregnancies are linked to risk factors, studies estimate that up to 50% of women diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy have no identifiable predisposing factors.
What Should You Do If You Suspect Ectopic Pregnancy?
Even in the absence of risk factors, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms like:
Abdominal or pelvic pain.
Unusual vaginal bleeding or spotting.
Dizziness, fainting, or shoulder pain.
Are there any symptoms associated with ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, an ectopic pregnancy often presents with specific symptoms, though they may vary in severity and timing. In the early stages, symptoms may resemble those of a normal pregnancy, but as the condition progresses, more distinct and potentially serious symptoms can occur.
Common Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
1. Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Missed period
Nausea or vomiting
Breast tenderness
These are typical pregnancy signs and may not indicate a problem.
2. Specific Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
As the ectopic pregnancy develops, the following symptoms may arise:
Abdominal or pelvic pain: Often on one side, the pain can be sharp, cramping, or persistent.
Vaginal bleeding or spotting: Irregular bleeding may occur, different from a normal menstrual period.
Shoulder tip pain: This can occur due to internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm, often a sign of advanced complications.
3. Signs of Tubal Rupture (Emergency Symptoms)
If the ectopic pregnancy grows large enough to rupture the fallopian tube or another structure, life-threatening symptoms may develop:
Sudden, severe abdominal pain.
Heavy vaginal bleeding.
Dizziness, fainting, or signs of shock (low blood pressure and rapid heart rate).
When Do Symptoms Appear?
Symptoms typically develop between the 4th and 12th week of pregnancy, although they can appear earlier or later depending on the pregnancy's location and progression.
Why Prompt Action Is Necessary
An ectopic pregnancy cannot develop into a viable pregnancy and can cause serious complications, including internal bleeding and damage to reproductive organs. If you experience these symptoms, particularly severe or sudden pain and heavy bleeding, seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
Doctors will use:
Ultrasound: To confirm the pregnancy's location.
Blood tests: To measure hCG levels, which may rise abnormally in ectopic pregnancies.
Key Takeaway
If you experience unusual pain or bleeding during pregnancy, do not ignore it. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing the condition and protecting your health.
How is ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy involves a combination of clinical evaluations, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Since the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can overlap with those of a normal early pregnancy or other medical conditions, accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications.
Steps in Diagnosing an Ectopic Pregnancy
1. Medical History and Symptoms Assessment
The doctor will ask about your symptoms, such as abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or irregular periods.
A history of risk factors like pelvic infections, prior ectopic pregnancies, or fallopian tube surgeries may raise suspicion.
2. Physical Examination
A pelvic exam helps identify areas of tenderness, masses, or signs of internal bleeding.
While this can provide clues, a physical exam alone cannot confirm an ectopic pregnancy.
3. Transvaginal Ultrasound
This is the primary imaging tool used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy.
A transvaginal ultrasound provides detailed images of the reproductive organs and is used to:
Determine whether a pregnancy is located inside the uterus.
Identify the presence of a gestational sac or abnormal tissue in the fallopian tube or other locations.
In some cases, the ultrasound may reveal a "pseudo-sac" in the uterus, which mimics a normal pregnancy.
4. Blood Tests for hCG Levels
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy.
In a normal pregnancy, hCG levels double approximately every 48-72 hours.
In ectopic pregnancies, hCG levels often rise more slowly or plateau, which can indicate an abnormal pregnancy.
Serial hCG measurements over a few days help in cases where the diagnosis is unclear.
5. Diagnostic Laparoscopy
If the ultrasound and hCG results are inconclusive, a diagnostic laparoscopy may be performed.
This minimally invasive surgery allows the doctor to directly view the fallopian tubes and other structures to confirm an ectopic pregnancy.
Key Points in Diagnosis
Early ectopic pregnancies may be difficult to detect because the gestational sac might not be visible on ultrasound until the hCG levels are above 1,500-2,000 mIU/mL.
If the pregnancy is too early to locate (a situation called a pregnancy of unknown location), doctors monitor hCG levels and repeat imaging tests.
Importance of Prompt Diagnosis
Timely diagnosis is critical because untreated ectopic pregnancies can lead to life-threatening complications, such as tubal rupture and internal bleeding. If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, seeking immediate medical care is essential.
How can ectopic pregnancy be treated?
1. Medication: Methotrexate
What It Is: Methotrexate is a medication that stops the growth of the rapidly dividing pregnancy cells.
When It’s Used:
The pregnancy is detected early.
The fallopian tube hasn’t ruptured.
The patient’s hCG levels are relatively low (usually below 5,000 mIU/mL).
How It’s Administered:
Given as an injection, often in a single dose.
Follow-up blood tests measure hCG levels to ensure they are declining until they reach zero.
Advantages:
Non-invasive and preserves the fallopian tubes for future pregnancies.
Side Effects:
Abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue, or mild spotting.
2. Surgery
What It Is: Surgical intervention to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair or remove damaged tissue.
When It’s Used:
The fallopian tube has ruptured, causing severe internal bleeding.
Medication isn’t appropriate or has failed.
The ectopic pregnancy is advanced.
Types of Surgery:
Laparoscopy:
Minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera.
Can involve removing the ectopic tissue while preserving the fallopian tube (salpingostomy) or removing the affected tube entirely (salpingectomy) if it’s severely damaged.
Laparotomy:
Open surgery performed in emergencies, such as when the tube has ruptured and bleeding is extensive.
3. Expectant Management (Rare)
What It Is: Monitoring without active treatment.
When It’s Used:
The ectopic pregnancy resolves on its own (e.g., hCG levels are declining, and no symptoms of rupture are present).
Considerations:
Frequent monitoring with blood tests and ultrasounds is required to ensure the pregnancy resolves completely.
After Treatment
Emotional Support: Many women experience emotional distress or grief after an ectopic pregnancy and may benefit from counseling or support groups.
Follow-Up:
Regular monitoring of hCG levels to confirm complete resolution of the pregnancy.
Addressing any underlying conditions, such as infections or tubal damage, to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Future Fertility and Pregnancy
Women can often conceive after an ectopic pregnancy, but the risk of recurrence is higher.
It’s advisable to consult a fertility specialist to evaluate tubal health and discuss future pregnancy planning.
Emergency Care
If a fallopian tube ruptures, it is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgery to stop internal bleeding and repair or remove the damaged tissue. Delayed treatment can be life-threatening.
Timely diagnosis and treatment are critical in managing ectopic pregnancy safely and preserving reproductive health.
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition in which a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. It is a non-viable pregnancy that poses significant risks to a woman’s health, including severe complications like internal bleeding if untreated.
While certain risk factors, such as previous pelvic infections, surgeries, or hormonal imbalances, can increase the likelihood of ectopic pregnancy, it can occur even in women without any known risk factors. Recognizing early symptoms such as pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, and shoulder tip pain, along with seeking prompt medical care, is essential for early diagnosis and treatment.
Advancements in diagnostic methods, including transvaginal ultrasounds and blood tests for hCG levels, have made it easier to detect ectopic pregnancies early. Treatment options, such as medication with methotrexate or surgical intervention, are effective in managing the condition, preventing complications, and preserving future fertility when possible.
Although experiencing an ectopic pregnancy can be physically and emotionally challenging, many women go on to have healthy pregnancies with proper medical care and support. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments empowers women to take proactive steps for their reproductive health and seek timely intervention when needed.