Different Types of sperm and their characteristics
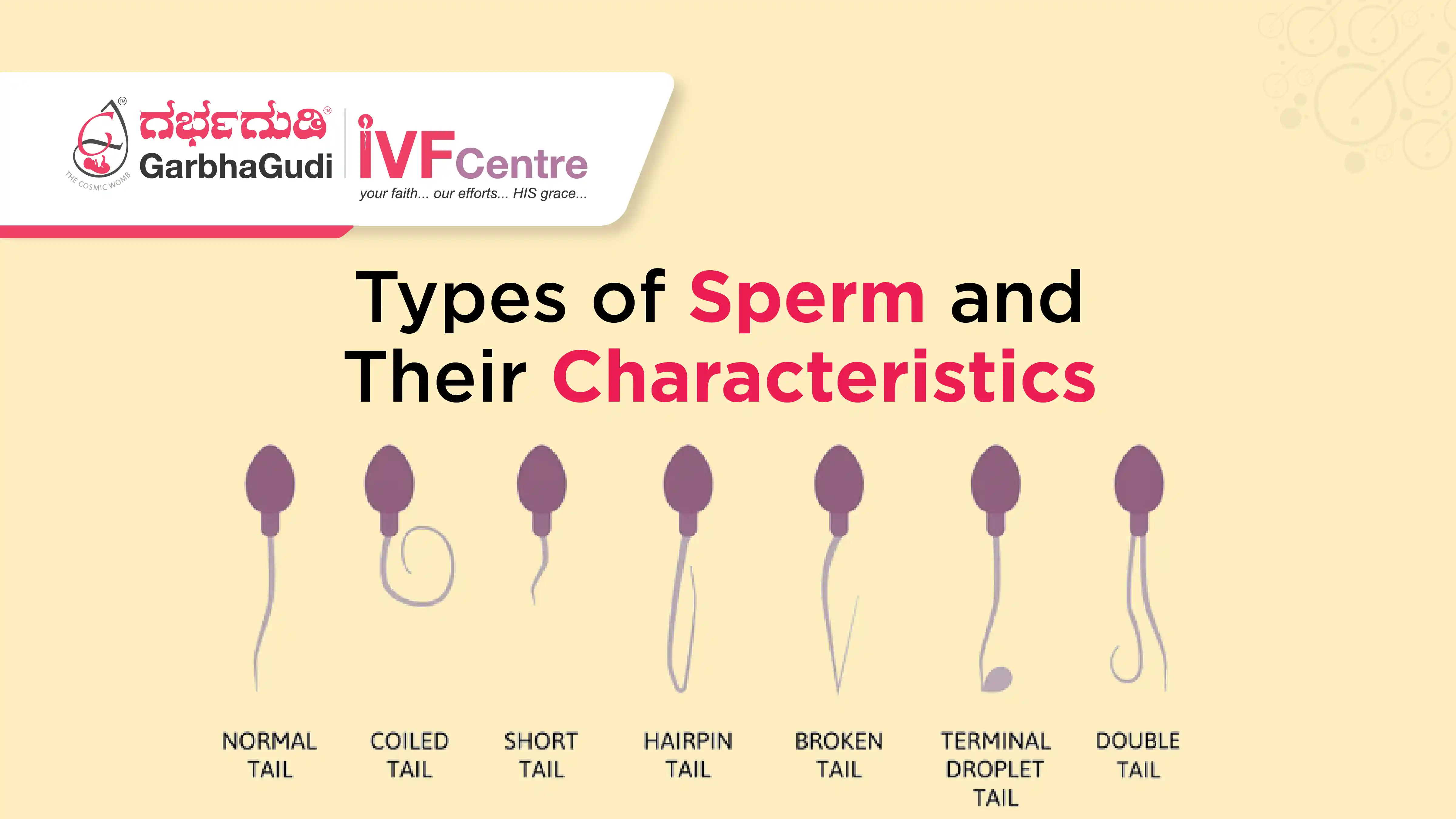
Sperm cells, also known as spermatozoa, are the male reproductive cells essential for fertilization and the continuation of genetic material. Although all sperm cells are designed to fertilize an egg, their characteristics can vary based on morphology, motility, and functionality. Understanding the different types of sperm is crucial for diagnosing fertility issues and improving reproductive health. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of sperm and their significance.
1. Normal Sperm (Healthy Sperm)
Structure: Normal sperm cells have three primary parts: an oval-shaped head, a midpiece, and a long, thin tail. The head contains the genetic material (DNA), the midpiece provides energy for movement, and the tail propels the sperm forward.
Function: Healthy sperm are characterized by their ability to swim efficiently toward the egg and fertilize it. This is crucial for natural conception.
Significance: The presence of a high percentage of normal sperm in a semen sample indicates good fertility potential.
How to Maintain Normal Sperm:
Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
Exercise regularly to improve blood flow and hormone regulation.
Avoid excessive heat exposure, which can damage sperm cells.
2. Abnormal Sperm
Characteristics: Abnormal sperm may have defects in their structure, such as:
Head abnormalities: Large, small, misshapen, or double-headed.
Midpiece abnormalities: Enlarged or defective midpieces.
Tail abnormalities: Coiled, double, or absent tails.
Impact on Fertility: Abnormal sperm may struggle to swim or penetrate the egg, reducing the chances of successful fertilization.
Causes of Abnormal Sperm:
Genetic factors.
Lifestyle choices like smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use.
Environmental exposure to toxins or radiation.
Medical conditions such as varicocele or hormonal imbalances.
Treatment Options:
Lifestyle modifications.
Antioxidant supplements.
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
3. Motile Sperm
Definition: Motile sperm are those that can actively move and swim toward the egg. Their ability to move is a critical factor for successful fertilization.
Types of Motility:
Progressive motility: Sperm move in a straight line or large circles.
Non-progressive motility: Sperm move but does not make significant forward progress.
Significance: High motility increases the likelihood of sperm reaching the egg and fertilizing it.
How to Improve Motility:
Consume foods rich in zinc, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption.
Stay hydrated to maintain optimal seminal fluid consistency.
4. Non-Motile Sperm
Definition: Non-motile sperm lack the ability to move and are often considered non-functional for natural conception.
Causes of Non-Motility:
Genetic abnormalities.
Prolonged exposure to heat.
Infections or inflammation in the reproductive system.
Hormonal imbalances.
Impact on Fertility: Non-motile sperm are unable to reach the egg, necessitating medical intervention for conception.
Medical Solutions:
Sperm washing techniques to isolate motile sperm.
ART methods like ICSI, where a single sperm is injected directly into the egg
5. Live Sperm
Characteristics: Live sperm are viable sperm cells capable of fertilizing an egg. The viability of sperm is an essential factor in fertility assessments.
Testing Viability: A sperm viability test is used to determine the percentage of living sperm in a semen sample. This is crucial for understanding fertility potential.
How to Increase Sperm Viability:
Avoid exposure to environmental toxins.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a nutrient-rich diet.
Address underlying medical conditions that may affect sperm health.
6. Dead Sperm
Characteristics: Dead sperm are non-viable cells that cannot fertilize an egg. A high percentage of dead sperm in a sample may indicate underlying health issues.
Causes of High Dead Sperm Count:
Poor diet and lack of antioxidants.
Exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation.
Prolonged periods of abstinence.
Infections or high scrotal temperature.
Impact on Fertility: A high percentage of dead sperm reduces overall fertility, often requiring medical evaluation and treatment.
Management:
Address lifestyle factors.
Seek medical advice for infections or other health concerns.
Utilize ART techniques to select viable sperm.
7. Y-Chromosome Sperm
Role: Responsible for producing male offspring.
Characteristics:
Smaller and lighter than X-chromosome sperm.
Faster swimmers but have a shorter lifespan compared to X-chromosome sperm.
Significance: Couples looking to influence the gender of their child often consider methods that might favor Y-chromosome sperm, though no guarantees exist.
Tips to Boost Y-Sperm Success (Theoretically):
Time intercourse closer to ovulation to take advantage of the Y-sperm's speed.
Maintain an alkaline vaginal environment, which may favor Y-sperm survival.
8. X-Chromosome Sperm
Role: Responsible for producing female offspring.
Characteristics:
Larger and slower compared to Y-chromosome sperm.
Longer lifespan, enabling them to survive longer in the female reproductive tract.
Significance: X-sperm are favored when intercourse occurs a few days before ovulation, as they can outlast Y-sperm.
Tips to Boost X-Sperm Success (Theoretically):
Time intercourse earlier in the fertility window.
Maintain an acidic vaginal environment, which may favor X-sperm survival.
Factors Affecting Sperm Quality
Sperm quality is influenced by several factors that determine the ability of sperm to fertilize an egg. Key factors include:
1. Diet and Nutrition:
Foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins (C, E), and minerals like zinc and selenium improve sperm quality.
Omega-3 fatty acids support sperm motility and viability.
2. Lifestyle Choices:
Avoid smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and recreational drugs, which negatively affect sperm health.
Manage stress through meditation or yoga.
3. Physical Activity:
Regular exercise improves blood flow and testosterone levels, supporting sperm production.
4. Environmental Exposure:
Limit exposure to toxins, pesticides, and radiation.
Avoid prolonged heat exposure, such as frequent sauna use or hot baths.
5. Medical Conditions:
Conditions like varicocele, infections, or hormonal imbalances can impact sperm health. Timely treatment is essential.
How to Assess Sperm Health?
A comprehensive semen analysis evaluates sperm quality and identifies potential issues. Key parameters include:
Sperm Count: Measures the number of sperm in a given sample.
Motility: Assesses the percentage of sperm that can swim effectively.
Morphology: Examines the shape and structure of sperm.
Viability: Determines the percentage of living sperm.
pH Levels: Indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the semen.
Treatment Options for Sperm-Related Issues
If fertility challenges are identified, several treatment options are available:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Improve diet and exercise routines.
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
2. Medical Treatments:
Medications to address hormonal imbalances or infections.
Surgical procedures like varicocele repair.
3. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is directly placed in the uterus to increase fertilization chances.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Sperm is combined with an egg in a lab setting.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into the egg.
When to Seek Medical Help?
If you or your partner are facing difficulties in conceiving, consult a fertility specialist. Signs to watch for include:
Low sperm count or poor motility in a semen analysis.
Persistent health issues or lifestyle factors that may affect fertility.
Prolonged attempts at conception without success.
Fertility clinics, such as GarbhaGudi IVF, offer advanced diagnostic and treatment options to address male fertility challenges effectively.
Understanding the different types of sperm and their characteristics is vital for diagnosing and treating fertility issues. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, addressing medical concerns, and seeking expert guidance, couples can improve their chances of conception. Whether through natural methods or assisted reproductive technologies, there are multiple paths to achieving parenthood. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and support on your fertility journey.