Exploring Advanced Biomarkers for Fertility Potential
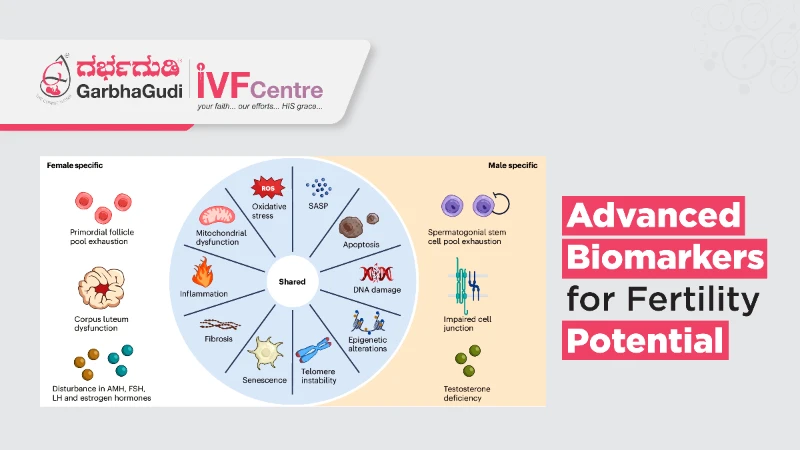
The science of fertility has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by a growing understanding of reproductive biology and the development of cutting-edge technologies. One of the most promising areas of research is the use of advanced biomarkers to assess fertility potential. Biomarkers, measurable indicators of biological processes, can provide valuable insights into reproductive health, helping individuals and clinicians make informed decisions about fertility treatments and family planning.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of advanced fertility biomarkers, explaining their significance, the science behind them, and their practical applications in modern reproductive medicine.
What Are Biomarkers in Fertility?
Biomarkers are biological molecules that can be measured to provide information about physiological or pathological processes in the body. In the context of fertility, biomarkers are indicators of reproductive health and can offer insights into ovarian reserve, sperm quality, hormonal balance, and overall reproductive potential.
These biomarkers are critical for diagnosing infertility, predicting the success of fertility treatments, and tailoring individualized care plans for patients.
Traditional Biomarkers in Fertility Assessment
Before exploring advanced biomarkers, it's essential to understand the traditional markers commonly used in fertility evaluations:
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Role: Regulates ovarian follicle growth in women and spermatogenesis in men.
Significance: High FSH levels may indicate diminished ovarian reserve or poor sperm production.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Role: Triggers ovulation in women and stimulates testosterone production in men.
Significance: Abnormal LH levels can indicate issues like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hypogonadism.
Estradiol (E2)
Role: A key estrogen hormone involved in ovulation and endometrial preparation.
Significance: Abnormal levels can affect ovulation and implantation.
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH)
Role: Reflects the size of the ovarian reserve.
Significance: A low AMH level suggests diminished ovarian reserve, while high levels may indicate PCOS.
Semen Analysis
Role: Evaluates sperm count, motility, and morphology.
Significance: Provides a snapshot of male fertility potential.
Advanced Biomarkers in Fertility Potential
While traditional biomarkers remain valuable, advanced biomarkers are offering deeper and more precise insights into fertility. Here are some cutting-edge biomarkers and their implications:
1. Inhibin B
Role: A hormone secreted by granulosa cells in women and Sertoli cells in men.
Significance:
In women: Indicates ovarian reserve and follicular activity.
In men: Reflects spermatogenic activity and testicular function.
2. Antral Follicle Count (AFC)
Role: Measured via ultrasound, it counts the number of antral follicles in the ovaries.
Significance: Provides a direct assessment of ovarian reserve and correlates with AMH levels.
3. DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI)
Role: Measures DNA integrity in sperm cells.
Significance:
High levels of DNA fragmentation are associated with infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, and poor embryo quality.
Helps identify male factor infertility that may not be evident in standard semen analysis.
4. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Semen
Role: ROS are byproducts of metabolism that can damage sperm cells.
Significance: Elevated ROS levels are linked to oxidative stress, which negatively impacts sperm quality and function.
5. Mitochondrial Biomarkers
Role: Evaluate mitochondrial function in eggs and sperm.
Significance: Mitochondrial dysfunction can impair egg quality, sperm motility, and embryo development.
6. Endometrial Receptivity Array (ERA)
Role: A genetic test that evaluates the receptivity of the endometrium.
Significance:
Determines the optimal timing for embryo transfer in IVF.
Improves implantation rates by aligning the embryo transfer with the endometrial window of receptivity.
7. Proteomics and Metabolomics
Role: Analyzes protein and metabolite profiles in reproductive tissues and fluids.
Significance:
Identifies molecular signatures associated with egg quality, sperm health, and endometrial receptivity.
Aids in understanding unexplained infertility.
8. Cumulus Cell Biomarkers
Role: Cumulus cells surround the egg and play a crucial role in its development.
Significance: The gene expression profiles of cumulus cells can indicate egg quality and predict IVF outcomes.
9. MicroRNA (miRNA) Biomarkers
Role: Small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression.
Significance:
miRNAs in follicular fluid, semen, or endometrial tissue can provide insights into ovarian function, sperm health, and implantation potential.
Applications of Advanced Biomarkers in Fertility Treatment
The use of advanced biomarkers is transforming the field of reproductive medicine. Here’s how they are being applied:
1. Personalized Fertility Treatment
Advanced biomarkers allow for a tailored approach to fertility care. For example, AMH and AFC can guide decisions on ovarian stimulation protocols, while ERA can optimize the timing of embryo transfer.
2. Improved Diagnosis
Biomarkers like DFI and ROS provide a more nuanced understanding of male infertility, while proteomics and metabolomics help uncover the root causes of unexplained infertility.
3. Enhanced IVF Success Rates
By identifying high-quality eggs, sperm, and embryos, as well as determining the ideal conditions for implantation, advanced biomarkers increase the likelihood of successful IVF outcomes.
4. Early Intervention
Biomarkers can detect signs of declining fertility early, enabling individuals to take proactive steps, such as fertility preservation through egg or sperm freezing.
Challenges and Future Directions
While advanced biomarkers hold great promise, there are challenges to consider:
Accessibility: Advanced testing can be expensive and may not be widely available.
Standardization: There is a need for standardized protocols and reference ranges for biomarker interpretation.
Ethical Considerations: The use of genetic and molecular testing raises ethical questions about privacy and decision-making in reproductive care.
Future research will likely focus on:
Developing non-invasive biomarkers, such as those detectable in blood or saliva.
Integrating artificial intelligence to analyze biomarker data and predict fertility outcomes.
Expanding our understanding of how environmental and lifestyle factors influence biomarker levels.
Advanced biomarkers are revolutionizing the way fertility potential is assessed and managed. By providing deeper insights into reproductive health, these biomarkers empower individuals and clinicians to make informed decisions and improve outcomes in fertility treatment.
As research continues to advance, the integration of biomarkers into routine fertility care promises a future of more personalized, efficient, and effective reproductive medicine. Whether you’re planning for parenthood or navigating infertility, understanding these biomarkers can be a valuable tool in your journey.
Share this page
About Us
GarbhaGudi is a chain of New-Generation Infertility Treatment Hospitals equipped with state-of- art-infrastructure & cutting-edge IVF Technology to address infertility issues & their emotional & mental effects on couples. We have a team of qualified & experienced doctors; their in-depth knowledge & expertise leaves no stone unturned to solve all your infertility issues. The Supportive & caring staff is always by your side to motivate & guide you throughout the journey. GarbhaGudi IVF, the best fertility treatment hospital in Bangalore, provides emotional support to couples facing infertility issues and sexual problems
Contact Us