How to Reduce Endometrial Thickness Naturally?
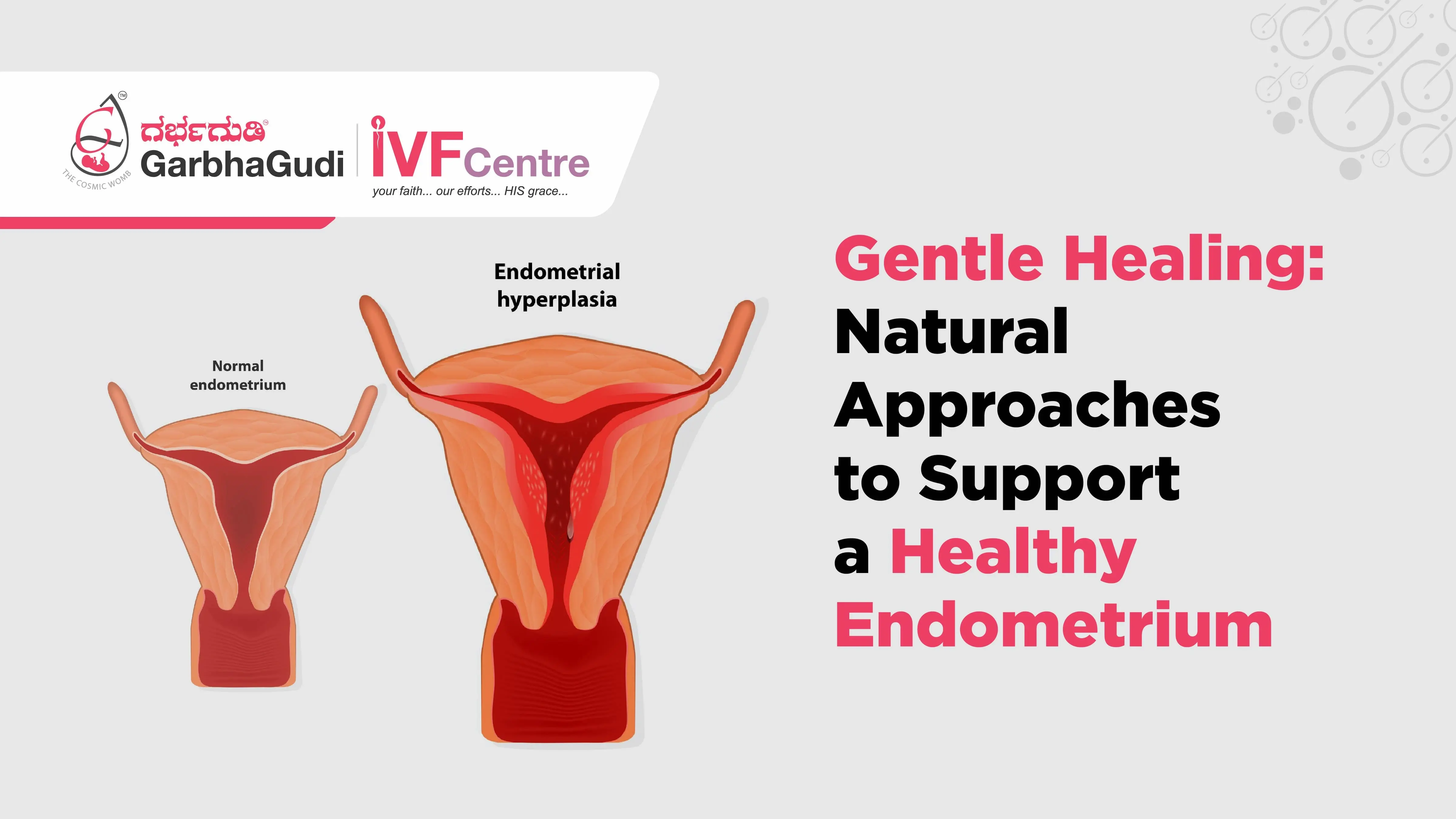
What is the endometrium, and why is it crucial for reproductive health?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, a tissue that undergoes dynamic changes throughout the menstrual cycle. Its crucial role in reproductive health lies in its response to hormonal fluctuations and its involvement in key reproductive processes.
Structural Changes: The endometrium thickens in response to rising estrogen levels during the first half of the menstrual cycle, preparing for a potential pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, the embryo seeks to implant into the richly vascularized and receptive endometrial lining.
Implantation Site: The endometrium serves as the implantation site for the fertilized egg. It provides essential nutrients and support for the early stages of embryonic development.
Menstrual Cycle Regulation: If pregnancy does not occur, hormonal shifts trigger the shedding of the endometrial lining during menstruation. This cyclical process of thickening, preparing for implantation, and shedding is fundamental to the menstrual cycle.
Hormonal Influence: The endometrium's responsiveness to hormonal changes, particularly estrogen and progesterone, is crucial for its proper development and maintenance. A balanced hormonal environment ensures the cyclic regeneration of the endometrial tissue.
Understanding the dynamic nature of the endometrium is essential for appreciating its significance in the reproductive journey. Any disruptions in the structure or function of the endometrium can impact fertility and reproductive health, emphasizing the importance of maintaining its well-being for those seeking a healthy reproductive outcome.
How can diet contribute to a healthy endometrium?
Diet plays a crucial role in nurturing a healthy endometrium, influencing its structure and overall reproductive function. Here are ways in which dietary choices can contribute to endometrial health:
1. Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall reproductive health. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to optimal endometrial function.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that may positively influence the endometrium. These fatty acids contribute to a healthy lipid profile and may enhance blood flow to the reproductive organs.
3. Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables, such as vitamin C and E, help combat oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can negatively impact reproductive tissues, and a diet rich in antioxidants supports a favorable environment for the endometrium.
4. Iron-Rich Foods: Adequate iron intake from sources like lean meats, beans, and dark leafy greens is essential for maintaining healthy blood levels. Iron supports proper oxygenation and circulation, crucial for the nourishment of the endometrial tissue.
5. Folic Acid: Foods containing folic acid, such as leafy greens, citrus fruits, and legumes, contribute to reproductive health. Folic acid is crucial for DNA synthesis and repair, processes vital for the development and maintenance of the endometrium.
6. Balanced Hormones: Some foods, like whole grains and flaxseeds, contain compounds that may help balance hormones, particularly estrogen. Maintaining hormonal balance is essential for the proper functioning of the endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle.
7. Hydration: Staying well-hydrated supports overall health and may indirectly contribute to a healthy endometrium. Proper hydration ensures optimal blood flow and nutrient delivery to reproductive tissues.
8. Limited Processed Foods: Minimizing the intake of processed foods, refined sugars, and excessive saturated fats is advisable. These dietary components may contribute to inflammation and hormonal imbalances that can impact endometrial health.
Adopting a well-balanced and nutrient-dense diet promotes not only overall health but also provides the necessary building blocks for a healthy endometrium. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice tailored to individual health needs and goals.
Can stress reduction techniques influence the health of the endometrium?
Yes, stress reduction techniques can play a significant role in positively influencing the health of the endometrium. Chronic stress has been linked to hormonal imbalances and physiological changes that can impact reproductive health. Implementing stress reduction techniques can contribute to a more supportive environment for the endometrium. Here's how:
1. Hormonal Balance: Stress activates the body's "fight or flight" response, leading to increased cortisol levels. Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones, potentially affecting the regularity and health of the endometrial lining. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help restore hormonal equilibrium.
2. Blood Flow: Stress-induced vasoconstriction can reduce blood flow to various organs, including the uterus. Practices like relaxation exercises and mindfulness may promote vasodilation, enhancing blood flow to the endometrium. Improved blood circulation supports nutrient delivery and overall tissue health.
3. Inflammation Reduction: Chronic stress is associated with increased inflammation in the body, which can negatively impact the endometrium. Stress reduction techniques have been linked to lower inflammatory markers, potentially creating a more favorable environment for a healthy endometrial lining.
4. Menstrual Regularity: Stress can contribute to irregular menstrual cycles, affecting the timing and thickness of the endometrium. Incorporating stress reduction practices into one's routine may contribute to more regular menstrual cycles, promoting the overall health of the endometrium.
5. Immune Support: Chronic stress can suppress the immune system, potentially influencing the immune response in the uterus. Stress reduction techniques support a robust immune system, which is vital for maintaining a healthy endometrium.
While stress reduction techniques offer potential benefits, individual responses can vary. It's essential to explore various methods, such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness, and identify what works best for personal well-being. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice on stress management strategies tailored to individual needs and health goals.
Supporting the Endometrium: The Crucial Role of Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for the optimal health and function of the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. Hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, orchestrate the cyclical changes in the endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. Here's how hormonal balance influences the endometrium:
1. Estrogen Dominance: During the first half of the menstrual cycle, rising estrogen levels stimulate the growth and thickening of the endometrium. An imbalance in estrogen levels, such as estrogen dominance, can lead to excessive growth and potentially contribute to conditions like endometrial hyperplasia.
2. Progesterone's Role: After ovulation, progesterone levels increase. Progesterone helps to stabilize the endometrium, preparing it for the potential implantation of a fertilized egg. Adequate progesterone is essential for maintaining the appropriate thickness and receptivity of the endometrial lining.
3. Menstrual Cycle Regulation: Hormonal balance ensures the proper sequence of events in the menstrual cycle. Estrogen primes the endometrium for potential pregnancy, while progesterone stabilizes and prepares it for implantation or, in the absence of pregnancy, for shedding during menstruation.
4. Endometrial Receptivity: Hormonal fluctuations impact the receptivity of the endometrium to an embryo. An optimal balance of estrogen and progesterone creates an environment conducive to successful implantation and early embryonic development.
5. Impact on Blood Flow: Estrogen, in coordination with progesterone, influences blood vessel development in the endometrium. This vascularization is essential for nutrient delivery and a supportive environment for potential pregnancies.
6. Prevention of Abnormal Growth: Hormonal balance helps prevent abnormal growth of the endometrium, reducing the risk of conditions like endometriosis or uterine fibroids. Estrogen and progesterone work in harmony to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation in the endometrial tissue.
7. Menstrual Regularity: Balanced hormone levels contribute to regular menstrual cycles. Irregularities in hormonal balance can result in irregular menstrual cycles, impacting the timing and health of the endometrial lining.
8. Pregnancy Support: If conception occurs, hormonal balance is vital for the maintenance of the endometrium during early pregnancy. A harmonious interplay between estrogen and progesterone is essential for sustaining the pregnancy until the placenta takes over hormone production.
Maintaining hormonal balance involves a delicate interplay between various factors, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries. Lifestyle factors, such as diet, stress management, and adequate sleep, can influence hormonal health. Seeking regular healthcare check-ups and consulting with a healthcare provider are crucial for addressing any hormonal imbalances and promoting the overall well-being of the endometrium.
Hydration and the Endometrium: Unveiling the Role of Adequate Water Intake
Hydration, often overlooked in discussions about reproductive health, plays a subtle yet crucial role in supporting the endometrium—the inner lining of the uterus that undergoes cyclical changes throughout the menstrual cycle. Adequate water intake influences various physiological processes that contribute to the overall well-being of the endometrial tissue.
1. Nutrient Transport:
Water is a primary component of blood, which serves as the transportation system for nutrients. Proper hydration supports the efficient delivery of essential nutrients to the endometrium, ensuring its nourishment and optimal function.
2. Blood Circulation:
Well-hydrated blood is more fluid, promoting smoother circulation. This enhanced blood flow is vital for the endometrium as it ensures the timely delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the uterine tissue, supporting its health and responsiveness to hormonal changes.
3. Detoxification:
Hydration aids in the removal of waste products and toxins from the body. This detoxification process is beneficial for the endometrium, preventing the accumulation of harmful substances that could potentially impact its structure and function.
4. Temperature Regulation:
The uterus, including the endometrium, is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Proper hydration contributes to effective thermoregulation, preventing overheating or excessive cooling of the reproductive organs. This thermal stability is essential for maintaining a conducive environment for the endometrium.
5. Lubrication and Comfort:
Hydration plays a role in maintaining the lubrication of various bodily systems, including the reproductive tract. This lubrication contributes to comfort during intercourse and may indirectly influence the health of the endometrium by supporting a healthy and functional reproductive environment.
6. Hormonal Balance:
Water is involved in the regulation of various hormonal processes. Hormonal balance is critical for the endometrium's cyclical changes, and proper hydration ensures that hormonal signaling occurs smoothly, avoiding disruptions that could impact the endometrial lining.
7. Menstrual Regularity:
Adequate hydration contributes to the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Consistent menstrual cycles are indicative of a well-functioning endometrium, and maintaining hydration levels can help support the predictability and health of the menstrual cycle.
8. General Well-Being:
Hydration is a fundamental aspect of overall health, influencing various bodily functions. A woman's general well-being, including her hydration status, can indirectly impact the health and resilience of the endometrium.
Conclusion
In the journey of reproductive health, the endometrium emerges as a pivotal player, responding dynamically to hormonal cues and orchestrating the delicate balance necessary for conception and overall well-being. As we delve into the multifaceted factors influencing endometrial health, including hydration and water intake, a holistic understanding of the interplay between bodily processes unfolds.
Hydration, often regarded as a routine aspect of daily life, reveals its nuanced impact on the endometrium. Beyond quenching thirst, adequate water intake becomes a cornerstone for nutrient transport, blood circulation, detoxification, and temperature regulation. The endometrium, reliant on these fundamental processes, thrives in an environment where hydration is a constant companion.
In the intricate choreography of reproductive processes, hormonal balance emerges as a maestro, guiding the endometrium through its cyclical transformations. Hydration plays a supporting role in maintaining this delicate hormonal equilibrium, ensuring smooth communication and responsiveness that characterize a healthy endometrial lining.
As we acknowledge the interconnectedness of hydration and endometrial health, it becomes evident that every sip of water contributes to the well-being of this essential uterine lining. From lubrication to menstrual regularity, from nutrient delivery to thermoregulation, hydration weaves its influence silently yet significantly.
In the pursuit of reproductive wellness, let us raise a collective awareness of the role hydration plays in nurturing the endometrium. Encouraging a lifestyle that embraces adequate water intake becomes a simple yet potent strategy for supporting the intricate reproductive processes that lay the foundation for the miracle of life. In the symphony of reproductive health, let hydration be the refreshing note that harmonizes with the rhythms of the endometrium, fostering an environment where fertility and well-being intertwine seamlessly.