Recognizing the Signs of Female InfertilityDisclaimer
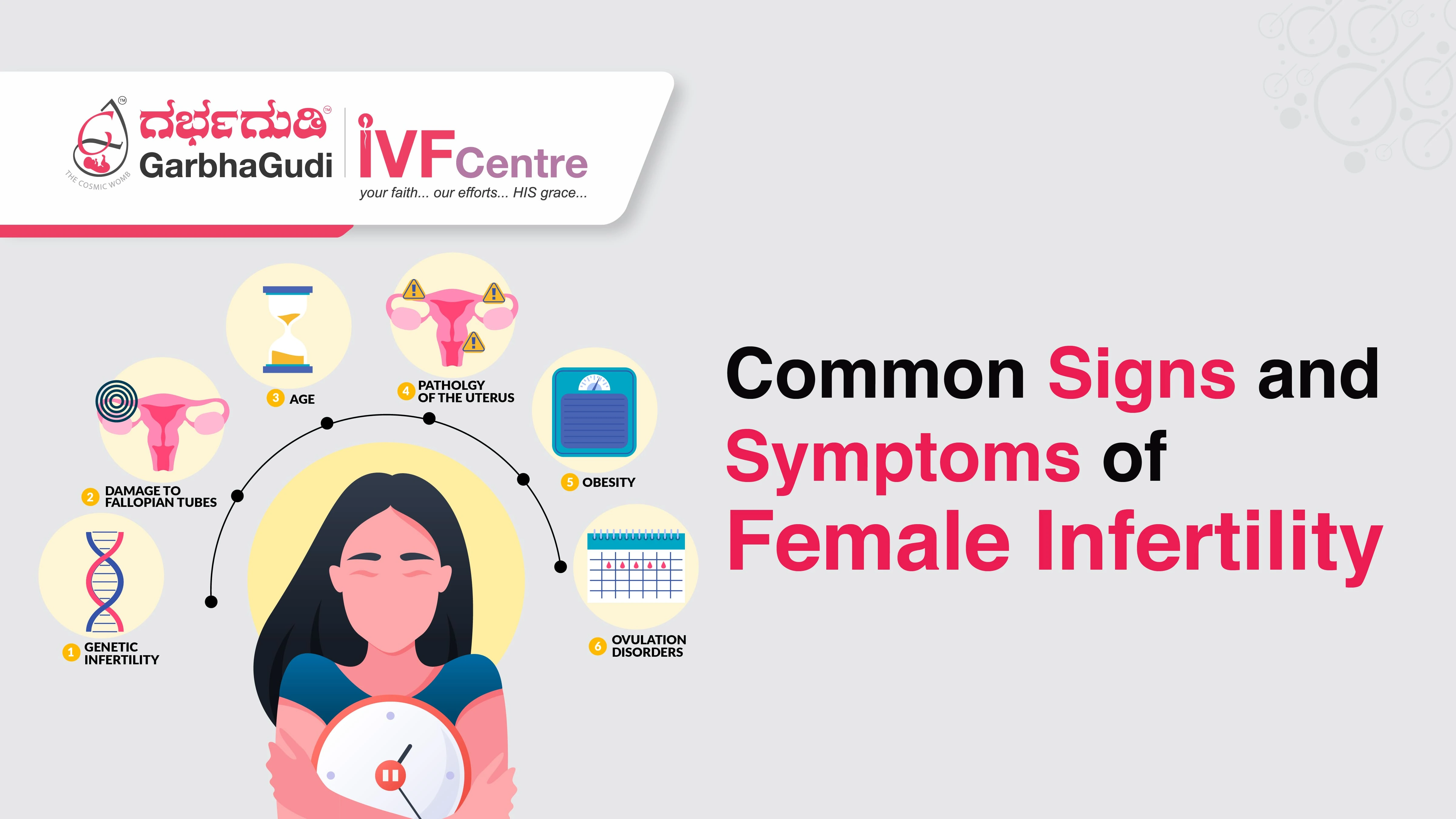
What are the common signs and symptoms of infertility in women?
Infertility in women can often be subtle, and many women may not experience obvious symptoms. However, there are several signs that could indicate a potential fertility issue. Common symptoms of infertility include:
Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Women with irregular periods may experience cycles that are shorter or longer than the typical 28-day cycle, or they may have no periods at all. Irregular cycles can affect ovulation, making it harder to conceive.
Heavy or Painful Periods:
Excessively painful or heavy periods could indicate underlying conditions like endometriosis or fibroids, both of which can interfere with fertility.
Excessive Hair Growth (Hirsutism):
Unexplained hair growth on areas such as the face, chest, or abdomen may be a sign of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that can lead to infertility.
Pelvic Pain:
Persistent pelvic pain, especially during intercourse or menstruation, can be a symptom of endometriosis, fibroids, or other reproductive health issues that impact fertility.
Unexplained Weight Gain or Difficulty Losing Weight:
Weight gain, particularly around the abdomen, or difficulty losing weight despite efforts, may be a sign of PCOS, which can disrupt hormone levels and affect fertility.
Acne or Skin Issues:
Skin problems like acne or oily skin can be linked to hormonal imbalances that could affect ovulation and fertility.
Pain During Intercourse:
Pain during intercourse can be a symptom of conditions like vaginal dryness, fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which may impact fertility.
Difficulty Conceiving:
The most direct symptom of infertility is the inability to conceive after trying for at least 12 months (or six months for women over 35). If conception hasn't occurred during this time, it may indicate underlying fertility issues.
Can Irregular Periods Indicate Infertility?
How Do Painful Periods Affect Fertility?
Painful periods, also known as dysmenorrhea, can sometimes be a sign of underlying conditions that affect fertility. While occasional menstrual cramps are common and usually not a cause for concern, severe or chronic pain during menstruation can indicate reproductive health issues that may impact a woman’s ability to conceive. Here's how painful periods can affect fertility:
Endometriosis:
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other organs in the pelvic area. This can cause severe menstrual pain and is a common cause of infertility. The tissue growth can interfere with ovulation, damage the fallopian tubes, and create an environment where fertilization is difficult.
Uterine Fibroids:
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy bleeding, pain during menstruation, and sometimes pain during intercourse. Fibroids can distort the shape of the uterus and affect implantation or even block the fallopian tubes, making it harder for sperm to reach the egg.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
PID is an infection of the reproductive organs, often caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It can cause chronic pelvic pain and damage to the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. This damage can significantly reduce fertility, as it may block the fallopian tubes or interfere with egg release.
Adenomyosis:
Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows into the uterine wall. It can cause painful, heavy periods and may lead to infertility by affecting the ability of the uterus to support a pregnancy.
Ovulatory Disorders:
In some cases, painful periods can be linked to ovulatory dysfunction, where the ovaries do not release eggs properly. Irregular or painful ovulation can result in difficulty conceiving, as the egg is not available for fertilization during the menstrual cycle.
When to Seek Medical Help for Painful Periods
If you experience painful periods, it's important to listen to your body and seek medical help in the following situations:
Severe Pain that Affects Daily Activities:
If menstrual pain is severe enough to interfere with your daily life—such as affecting work, school, or social activities—it's a sign that something may be wrong and you should consult a healthcare provider.
Chronic Pain Over Several Cycles:
If you experience persistent, recurring pain with each menstrual cycle that doesn't improve with over-the-counter pain relief, it could be an indication of an underlying condition such as endometriosis, fibroids, or adenomyosis.
Pain Accompanied by Heavy Bleeding:
If your periods are excessively heavy or involve clotting, and you experience pain that worsens over time, it’s important to seek medical advice. Heavy bleeding and pain can be associated with conditions like fibroids or PCOS.
Pain During Intercourse or Ovulation:
If you experience pain during sex or ovulation, it could be a sign of underlying issues like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or endometriosis. These conditions can affect fertility and should be diagnosed and treated early.
Pain That Starts Before Menstruation or Lasts After It Ends:
If you experience pain before your period begins or after it ends, it could be indicative of a condition like endometriosis or ovulatory disorders. This type of pain is not typical and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Difficulty Conceiving Along with Pain:
If you're trying to conceive and also experiencing painful periods, it’s a good idea to consult a fertility specialist. Painful periods could be a sign of underlying fertility issues that may require further evaluation and treatment.
What to Expect During a Medical Evaluation:
A doctor will typically conduct a thorough examination, which may include:
Physical examination to check for signs of pelvic conditions.
Ultrasound or MRI to examine the uterus, ovaries, and other reproductive organs.
Laparoscopy (a minor surgical procedure) to diagnose conditions like endometriosis.
Blood tests to check for hormonal imbalances or other underlying issues.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing painful periods and preventing fertility complications. If you experience any of the above symptoms, it's important to seek medical advice sooner rather than later.
Can pelvic pain be linked to infertility?
Yes, pelvic pain can be linked to infertility. Persistent or severe pelvic pain is often a symptom of underlying reproductive health issues that can interfere with a woman’s ability to conceive. Some of the conditions that can cause both pelvic pain and infertility include:
Endometriosis:
In endometriosis, tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs. This can cause severe pelvic pain, especially during menstruation. The tissue growth can lead to scarring, block fallopian tubes, and disrupt ovulation, making it more difficult to conceive.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
PID is an infection of the reproductive organs, typically caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It can cause chronic pelvic pain and lead to scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, which may prevent the sperm from reaching the egg or the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus.
Uterine Fibroids:
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. While they may not always cause infertility, large fibroids or fibroids located in certain areas of the uterus can affect implantation, cause abnormal uterine contractions, or block fallopian tubes, all of which can hinder conception.
Adenomyosis:
Adenomyosis occurs when the tissue that lines the uterus grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can cause severe menstrual cramps, pelvic pain, and abnormal bleeding. Adenomyosis can interfere with implantation, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant in the uterus.
Ovarian Cysts:
Ovarian cysts, particularly large ones or those that cause torsion (twisting of the ovary), can result in pelvic pain. While many cysts are harmless, certain types can disrupt ovulation or cause other complications that affect fertility.
Scar Tissue (Adhesions):
Scar tissue from previous surgeries, infections, or conditions like endometriosis can cause adhesions in the pelvic area. These adhesions can distort or block the fallopian tubes or uterus, leading to infertility.
Are there lifestyle factors that can cause infertility symptoms in women
Yes, several lifestyle factors can contribute to infertility symptoms in women. These factors can affect hormonal balance, ovulation, and overall reproductive health, making it more difficult to conceive. Here are some common lifestyle factors that can impact fertility in women:
1. Poor Diet and Nutrition:
A poor diet, especially one high in processed foods, unhealthy fats, and low in essential vitamins and minerals, can disrupt hormonal balance and ovulation. Deficiencies in nutrients like folic acid, iron, and vitamin D can negatively impact fertility. Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can support reproductive health.
2. Being Overweight or Underweight:
Overweight: Excess body fat can disrupt hormone levels, leading to irregular periods and problems with ovulation. It can also increase the risk of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is linked to infertility.
Underweight: Being too thin can also cause hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular periods or a lack of ovulation. Low body weight can result from eating disorders or excessive exercise, both of which can hinder fertility.
3. Excessive Exercise:
While moderate exercise is beneficial for overall health, excessive exercise, particularly in athletes, can lead to low body fat, hormonal imbalances, and disruption of ovulation. Women who engage in high-intensity exercise without adequate rest may experience amenorrhea (the absence of periods), which can impair fertility.
4. Smoking:
Smoking can have a significant impact on fertility by damaging the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and cervix, making it harder for an egg to be fertilized and for the embryo to implant in the uterus. Smoking can also reduce egg quality and increase the risk of miscarriage.
5. Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with hormone levels, disrupt ovulation, and lower the chances of conception. Even moderate drinking may negatively affect fertility in some women. Limiting alcohol intake or avoiding it completely is recommended when trying to conceive.
6. High Levels of Stress:
Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, particularly in the levels of cortisol and other stress-related hormones. This can interfere with ovulation and disrupt the menstrual cycle. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate rest can help improve fertility.
7. Exposure to Environmental Toxins:
Environmental pollutants, chemicals, and toxins (such as pesticides, heavy metals, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals) can negatively affect reproductive health. These substances can interfere with hormone production and disrupt ovulation and egg quality.
8. Lack of Sleep:
Sleep deprivation can affect the balance of reproductive hormones, including those involved in ovulation. Chronic lack of sleep can also contribute to stress and other factors that negatively impact fertility.
9. Caffeine Consumption:
High caffeine intake has been associated with reduced fertility in some women, though the exact relationship is not entirely clear. It's generally recommended to limit caffeine to moderate levels when trying to conceive.
10. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
Unprotected sex can lead to the transmission of STIs, some of which can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), scarring of the fallopian tubes, and damage to the reproductive organs, all of which can lead to infertility.
When should I see a doctor if I suspect infertility?
If you suspect infertility, it’s important to consult a doctor or fertility specialist at the right time to ensure proper evaluation and timely treatment. Here are some general guidelines on when to see a doctor:
1. If You’ve Been Trying to Conceive for Over a Year Without Success:
For women under 35: If you’ve been trying to conceive for a year or more without success, it's a good idea to seek medical advice. At this point, a doctor can help assess possible causes of infertility and provide guidance on the next steps.
For women 35 and older: If you’re over 35, it's recommended to seek help after six months of trying to conceive. Age-related fertility declines make it more important to consult a doctor earlier to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment.
2. If You Have Irregular or Absent Periods:
Irregular cycles or no periods at all can indicate ovulation problems or hormonal imbalances, which can make it difficult to conceive. If your menstrual cycle is inconsistent or if you’re experiencing amenorrhea (no periods), it’s time to see a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
3. If You Experience Painful Periods or Pain During Intercourse:
Severe menstrual pain or pain during sex can be signs of underlying conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can affect fertility. If these symptoms are persistent or severe, consult a doctor to determine the cause.
4. If You Have a History of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) or Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
PID or untreated STIs can lead to scarring or damage to the fallopian tubes, ovaries, or uterus, affecting fertility. If you have a history of these conditions, it’s important to seek medical advice to assess any potential damage that could impact your ability to conceive.
5. If You Have a History of Miscarriages:
Recurrent miscarriages or multiple pregnancy losses can indicate an underlying issue that affects fertility. If you've experienced more than two miscarriages, consult a fertility specialist to investigate potential causes such as hormonal imbalances, immune issues, or uterine problems.
6. If You Notice Changes in Your Skin, Hair, or Weight:
Sudden weight gain or loss, excessive hair growth, acne, or other physical changes could indicate hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is a common cause of infertility. If you notice these changes, it’s important to discuss them with a doctor.
7. If You Have a Known Medical Condition That Could Affect Fertility:
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, or autoimmune diseases, can affect fertility. If you have one of these conditions and are struggling to conceive, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for management and fertility guidance.
8. If You’re Overweight or Underweight:
Both extremes of body weight can affect fertility. Being underweight or overweight can lead to hormonal imbalances, irregular ovulation, and difficulty conceiving. If you're struggling to conceive and have concerns about your weight, consult a doctor for guidance on how to optimize your fertility.
9. If You’re Over 40:
Women over 40 often experience a decline in fertility due to age-related changes in egg quality and quantity. If you’re over 40 and struggling to conceive, it's important to see a doctor early to assess your fertility and discuss potential treatment options.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help:
Severe pelvic pain or heavy bleeding outside of your regular menstrual cycle could signal an emergency, such as an ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cyst rupture, or other reproductive health issues. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
What to Expect During a Fertility Consultation:
A fertility specialist will likely perform a comprehensive evaluation, which may include:
Medical history review to understand underlying health conditions and lifestyle factors.
Physical examination to check for reproductive health issues.
Blood tests to assess hormone levels.
Ultrasound or imaging to examine the reproductive organs, such as ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
Semen analysis for male partners to evaluate sperm health and quantity.
Can infertility symptoms be prevented or treated?
Infertility symptoms themselves can't always be fully prevented, but many underlying causes of infertility can be managed or treated with medical intervention, lifestyle changes, or both. Treatment options and prevention strategies largely depend on the cause of infertility and can vary between individuals. Here’s how infertility symptoms can be addressed:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Diet and Nutrition: Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet can support fertility. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate hormone levels, promote regular ovulation, and improve overall reproductive health. Avoiding excessive processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can also be beneficial.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or underweight can affect fertility. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition and regular exercise can help restore hormonal balance and improve the chances of conception.
Exercise: Moderate physical activity is important for overall health. However, excessive exercise can negatively impact fertility, especially in women who are underweight or have low body fat. It’s essential to find a balance that supports both health and fertility.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and disrupt ovulation. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular exercise can help manage stress and improve fertility.
Smoking and Alcohol Avoidance: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can reduce fertility in both men and women. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can improve reproductive health and fertility outcomes.
2. Medical Treatments for Infertility:
Hormonal Treatments: For women with hormonal imbalances (such as those with polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS), doctors may prescribe medications to regulate ovulation, such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins.
Fertility Medications: Medications like clomiphene citrate (Clomid), letrozole, or injectable hormones can stimulate ovulation in women who have irregular or absent ovulation.
Surgery: In cases where physical issues like fibroids, endometriosis, or blocked fallopian tubes are contributing to infertility, surgery may be an option to remove or treat the underlying issue.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): This is a procedure in which sperm is directly placed into the uterus during ovulation to increase the chances of pregnancy.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a common and highly effective treatment for many types of infertility. It involves stimulating the ovaries to produce eggs, which are then fertilized in the lab before being implanted into the uterus.
Egg or Sperm Donation: In cases of low egg quality or male infertility, egg or sperm donation may be an option to help achieve pregnancy.
3. Addressing Underlying Health Conditions:
Thyroid Issues: Thyroid imbalances, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can interfere with fertility. Proper treatment with medication can help regulate thyroid levels and improve fertility.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a common cause of infertility due to hormonal imbalances that affect ovulation. Medications, weight management, and lifestyle changes can help manage PCOS symptoms and improve fertility.
Endometriosis: Though endometriosis cannot be cured, treatments such as hormonal therapy or surgery can help manage symptoms and improve fertility.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): PID can cause scarring that affects fertility. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent further damage and improve the chances of conception.
4. Medical Interventions for Male Infertility:
Sperm Retrieval: In cases of low sperm count or motility, sperm retrieval techniques such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can be used in combination with IVF.
Surgery for Varicocele: A varicocele, or enlarged veins in the scrotum, can affect sperm quality. Surgery to correct this condition can improve fertility in some men.
Hormonal Treatment: In some cases, hormone therapy can help boost sperm production in men with hormonal imbalances.
5. Psychological Support:
Counseling: Infertility can cause emotional distress, so counseling or joining a support group can help individuals and couples cope with the emotional and psychological impact of infertility. This can also be particularly helpful for women who are undergoing treatments like IVF or IUI.
Prevention Strategies:
While not all infertility symptoms can be prevented, certain steps can reduce the risk of developing conditions that lead to infertility:
Early detection and treatment of STIs: Protecting yourself from sexually transmitted infections and getting regular check-ups can help prevent infections that can lead to PID and infertility.
Regular health screenings: Regular gynecological exams and check-ups can detect conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, or hormonal imbalances early, making them easier to treat.
Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins: Limiting exposure to chemicals, pesticides, and other harmful substances can protect reproductive health.
Prenatal care: Taking folic acid before and during pregnancy can help prevent birth defects and improve fertility.
Conclusion:
Infertility symptoms can often be treated or managed with medical interventions, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both. Early detection, addressing underlying medical conditions, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking professional help can improve fertility and the chances of conception. It's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the cause of infertility and the most suitable treatment options based on individual circumstances.