Understanding the Role of FSH in Women’s Fertility: What You Need to Know
For many women, the journey toward understanding fertility can be a confusing and emotional process. One key hormone that plays a significant role in female reproductive health is FSH, or Follicle-Stimulating Hormone. If you’re navigating fertility challenges, have undergone fertility testing, or are simply curious about your reproductive health, understanding FSH is an important part of the puzzle.
In this blog, we’ll explore what FSH is, how it impacts fertility, how it’s tested, and how to interpret the results. Whether you're trying to conceive or planning for the future, this information can give you a better understanding of your reproductive health and the factors influencing your fertility.
What is FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone)?
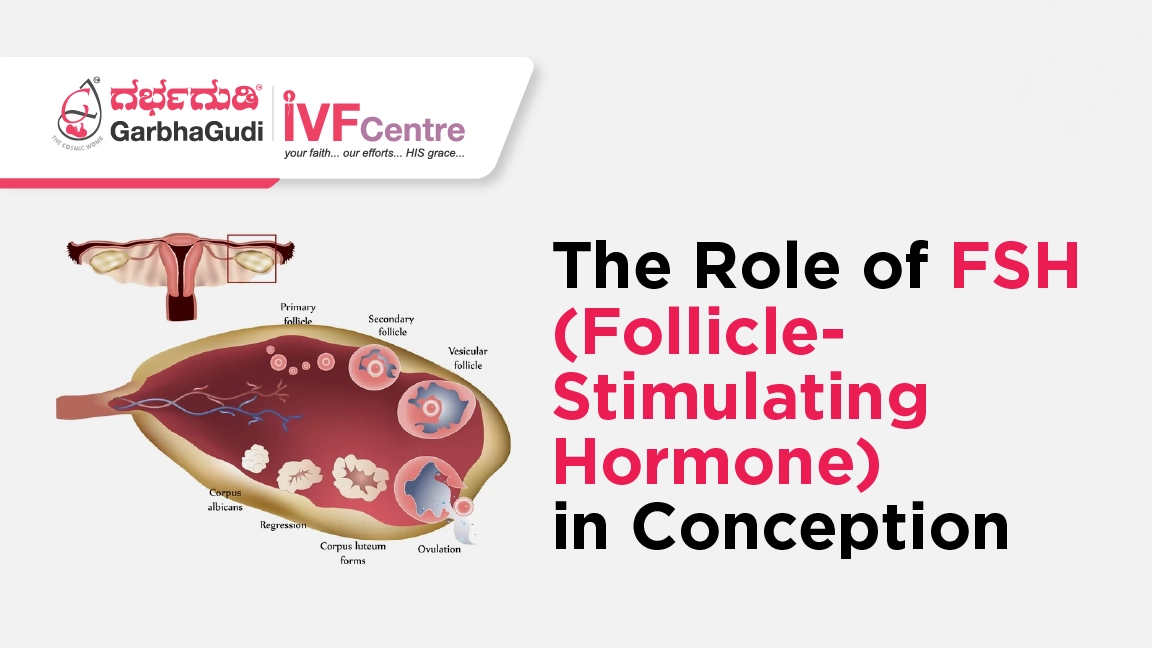
FSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, which is located at the base of your brain. It’s responsible for stimulating the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles—tiny sacs that contain the eggs—in women. The main role of FSH is to help regulate the menstrual cycle and play a critical role in ovulation.
Each month, a woman’s ovaries contain several follicles, but typically only one becomes dominant and releases an egg during ovulation. FSH helps in selecting and growing these follicles, preparing them for ovulation. This process is tightly controlled by other hormones like estrogen and progesterone, creating a delicate balance that drives the female reproductive system.
FSH levels can fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, peaking just before ovulation. Additionally, FSH is often measured during fertility testing, as abnormal levels can indicate underlying fertility issues. Understanding how FSH interacts with other hormones is key to understanding its role in fertility.
How FSH Impacts Fertility
FSH plays a direct role in ovulation, which is essential for conception. If a woman is trying to get pregnant, FSH is one of the most important hormones involved. Here's how it affects fertility:
Regulating the Menstrual Cycle: FSH works in tandem with other hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH), to regulate the menstrual cycle. It promotes the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles, each containing an egg. As FSH levels rise, the follicles mature, and one eventually becomes the dominant follicle, ready to release an egg during ovulation.
Signaling Ovulation: After the follicles mature, FSH helps signal the body to release the egg from the ovary. This process, known as ovulation, is necessary for pregnancy to occur. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. If no fertilization occurs, the egg is absorbed by the body, and the cycle begins again.
Egg Quantity and Quality: While FSH primarily influences the growth of individual follicles, it can also indicate the overall health of a woman’s ovarian reserve. As women age, their ovarian reserve decreases, leading to a rise in FSH levels. This can signal that fewer eggs are available for ovulation, and the quality of those eggs may also be lower, affecting the chances of conception.
FSH and Ovarian Reserve: What FSH Levels Tell You
One of the most important factors influencing fertility is a woman’s ovarian reserve—the number and quality of eggs she has available for fertilization. FSH levels can offer insight into this, especially as women approach their 30s and 40s.
When a woman’s ovarian reserve decreases, her ovaries need more stimulation to mature and release eggs. This results in higher levels of FSH in the bloodstream. A blood test to measure FSH levels is often used to assess a woman’s ovarian reserve and provide insight into her fertility potential. Here’s what FSH levels can indicate:
Low FSH levels: In a young, healthy woman, low FSH levels are ideal. Low levels suggest that the ovaries are functioning well and producing eggs regularly. Low FSH is often seen in women with normal ovarian reserve.
Elevated FSH levels: Higher FSH levels, particularly when measured early in the menstrual cycle (usually on day 3), may indicate that a woman’s ovarian reserve is lower. High FSH levels suggest that the ovaries are not responding well to hormonal signals, which could mean that fewer eggs are available. High levels may also be linked to conditions like primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) or perimenopause.
Very high FSH levels: Extremely high FSH levels may indicate that the ovaries are no longer functioning properly, which is often seen in women entering menopause. In such cases, the body may struggle to produce mature eggs, and fertility treatments may be required to support conception.
For many women, FSH levels are just one part of the fertility picture. While high FSH levels may indicate a challenge in conceiving, they don’t necessarily mean that pregnancy is impossible. IVF and other fertility treatments can help many women with high FSH levels conceive, depending on other factors like age, egg quality, and overall reproductive health
FSH Testing and When It’s Done
FSH testing is an important part of fertility evaluations, especially for women who are struggling to conceive. It’s commonly performed as part of an assessment of ovarian reserve and overall reproductive health. The test is typically done on day 3 of a woman’s menstrual cycle, when FSH levels are at their baseline. It’s important to note that FSH levels can fluctuate from cycle to cycle, so testing on the correct day is key for accurate results.
Here’s what happens during an FSH test:
Blood Sample: A blood sample is drawn from your arm, typically on day 3 of your menstrual cycle.
FSH Measurement: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory, where the FSH levels are measured. Your healthcare provider will use the results to determine how well your ovaries are functioning.
Interpreting Results: FSH levels are interpreted in conjunction with other fertility tests, such as an ultrasound, to assess your ovarian reserve and potential for conception. Your doctor will explain the results and may suggest treatment options based on your individual needs.
It’s important to keep in mind that while FSH testing is a valuable tool, it doesn’t give the full picture of your fertility. Additional tests, like AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) testing and ultrasound, may also be performed to assess your overall reproductive health.
FSH and Age: The Impact of Aging on Fertility
As women age, their fertility naturally declines. This decline is partly due to a decrease in ovarian reserve—the number of eggs available for fertilization. As ovarian reserve diminishes, FSH levels rise. This is why FSH testing is often used to assess fertility in women over the age of 35, as this is the age when fertility starts to decline more rapidly.
In younger women, low FSH levels indicate that the ovaries are functioning optimally. However, as a woman’s age increases, her ovarian reserve naturally decreases, leading to higher FSH levels. Elevated FSH levels can be a sign that the ovaries need more stimulation to produce eggs, making it harder for women to conceive naturally. This is one reason why fertility treatments, such as IVF, may be recommended for women with elevated FSH levels.
The rise in FSH levels with age can also be a sign of other fertility conditions, such as perimenopause or diminished ovarian reserve. If you are in your 30s or 40s and concerned about fertility, talking to a reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist can help you understand what your FSH levels mean for your fertility.
What Can You Do if Your FSH Levels Are High?
If your FSH levels are high, it can feel discouraging, but it’s important to remember that it doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible. Many women with high FSH levels have successfully conceived, especially with the help of fertility treatments.
Here are some options that may be available if your FSH levels are high:
IVF with Your Own Eggs: Even if you have higher FSH levels, you may still be able to produce eggs for IVF. Your fertility specialist will work with you to optimize your ovarian function through medications and monitoring.
Lifestyle Changes: While FSH levels can’t be reduced naturally, improving your overall health can support your fertility. Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can all positively impact your reproductive health.
Egg Freezing: If you’re not yet ready for pregnancy but want to preserve your fertility, egg freezing may be an option. This allows you to freeze healthy eggs while you’re still in your prime reproductive years.
Conclusion: The Bigger Picture of Fertility
FSH is a key player in female fertility, and understanding its role is crucial for women navigating their fertility journey. While FSH levels provide insight into ovarian reserve and reproductive health, they are just one piece of the puzzle. Many factors influence fertility, including age, lifestyle, and overall health. If you’re concerned about your fertility or have been told that your FSH levels are high, remember that there are options and treatments available.
Your fertility journey is uniquely yours, and understanding the role of FSH can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and family planning. Whether you’re trying to conceive naturally or exploring fertility treatments, having the right information can help you feel more confident and less anxious about the road ahead.
Remember, no matter where you are in your fertility journey, you’re not alone. There are specialists, support systems, and treatments designed to guide and help you achieve your dream of becoming a parent.